Education: The Ocean's Influence on Climate
 |
 |
 |
How Does the Ocean Influence Climate?
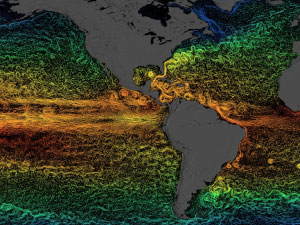
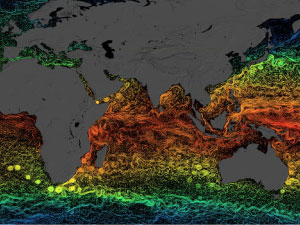
Aquarius measured ocean surface salinity, a climate-sensitive variable that - along with satellites that measure ocean currents, sea surface
temperature, winds, and ocean color - helps scientists study how global ocean circulation responds to climate change. Why salinity? Changes
in ocean saltiness can affect the density of water and play a major role in ocean circulation. Along with dissolved salt, these currents
move heat around the globe. Heat that is carried by the ocean affects wind and cloud formation in the atmosphere. Thus ocean heat controls
climate, no matter how far you live from the shore. As important, as salinity is a key surface tracer of fresh water input to output
from the ocean, Aquarius also provided much-needed information for global water cycle research.Featured Movie: Aquarius Pre-Launch Mission Overview
Hands-On Activities
- Coastal Versus Inland Temperatures
- Gathering, Analyzing, and Interpreting Environmental Data About the Ocean's Effects on Climate
- Global Winds and Ocean Currents
- Ocean Currents and Coastal Temperatures
Online Activities
- Annual Mean Data
- Changes in Annual Mean Data
- Ocean Motion: Ocean Surface Winds
- Changes in Monthly Mean Data
Movies
- Fluids that Moderate Climate
- Ocean Overturning and Heat Distribution
- Salinity and Climate
- Salt of the Earth: Climate Change Impacts on Salinity
- Salt of the Earth: Ocean Atmosphere Circulation Helps Moderate Climate
Podcasts
Articles & Documents